
Different generic functions for class MAMS.
generic.RdGeneric functions for summarizing an object of class MAMS.
Usage
# S3 method for MAMS
print(x, digits=max(3, getOption("digits") - 4), ...)
# S3 method for MAMS
summary(object, digits=max(3, getOption("digits") - 4), ...)
# S3 method for MAMS
plot(x, col=NULL, pch=NULL, lty=NULL, main=NULL, xlab="Analysis",
ylab="Test statistic", ylim=NULL, type=NULL, las=1, ...)
# S3 method for MAMS.sim
print(x, digits=max(3, getOption("digits") - 4), ...)
# S3 method for MAMS.sim
summary(object, digits=max(3, getOption("digits") - 4), ...)
# S3 method for MAMS.stepdown
print(x, digits=max(3, getOption("digits") - 4), ...)
# S3 method for MAMS.stepdown
summary(object, digits=max(3, getOption("digits") - 4), ...)
# S3 method for MAMS.stepdown
plot(x, col=NULL, pch=NULL, lty=NULL, main=NULL, xlab="Analysis",
ylab="Test statistic", ylim=NULL, type=NULL, bty="n", las=1, ...)Arguments
- x
An output object of class MAMS.
- digits
Number of significant digits to be printed.
- object
An output object of class MAMS.
- col
A specification for the default plotting color (default=
NULL). Seeparfor more details.- pch
Either an integer specifying a symbol or a single character to be used as the default in plotting points (default=
NULL). Seeparfor more details.- lty
A specification for the default line type to be used between analyses (default=
NULL). Setting to zero supresses ploting of the lines. Seeparfor more details.- main
An overall title for the plot (default=
NULL).- xlab
A title for the x axis (default=
"Analysis").- ylab
A title for the y axis (default=
"Test statistic").- ylim
Numeric vector of length 2, giving the y coordinates range (default=
NULL).- type
Type of plot to be used (default=
NULL). Seeplotfor more details.- bty
Should a box be drawn around the legend? The default
"n"does not draw a box, the alternative option"o"does.- las
A specification of the axis labeling style. The default
1ensures the labels are always horizontal. See?parfor details.- ...
Further (graphical) arguments to be passed to methods.
Details
print.MAMS produces a summary of an object from class MAMS including boundaries and requires sample size if initially requested.
summary.MAMS produces same output as print.MAMS.
plot.MAMS produces as plot of the boundaries.
print.MAMS.sim produces a summary of an object from class MAMS.sim including type-I-error and expected sample size.
summary.MAMS.sim produces same output as print.MAMS.sim.
print.MAMS.stepdown produces a summary of an object from class MAMS including boundaries and requires sample size if initially requested.
summary.MAMS.stepdown produces same output as print.stepdown.mams.
plot.MAMS.stepdown produces a plot of the boundaries. When used with stepdown.update, pluses indicate observed values of test statistics.
References
Magirr D, Jaki T, Whitehead J (2012) A generalized Dunnett test for multi-arm multi-stage clinical studies with treatment selection. Biometrika, 99(2), 494-501.
Stallard N, Todd S (2003) Sequential designs for phase III clinical trials incorporating treatment selection. Statistics in Medicine, 22(5), 689-703.
Magirr D, Stallard N, Jaki T (2014) Flexible sequential designs for multi-arm clinical trials. Statistics in Medicine, 33(19), 3269-3279.
Examples
# \donttest{
# 2-stage design with triangular boundaries
res <- mams(K=4, J=2, alpha=0.05, power=0.9, r=1:2, r0=1:2, p=0.65, p0=0.55,
ushape="triangular", lshape="triangular", nstart=30)
#>
#> i) find lower and upper boundaries
#>
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#>
#> ii) define alpha star
#> iii) perform sample size calculation
#> (maximum iteration number = 259)
#>
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> .
#> 50
#>
#>
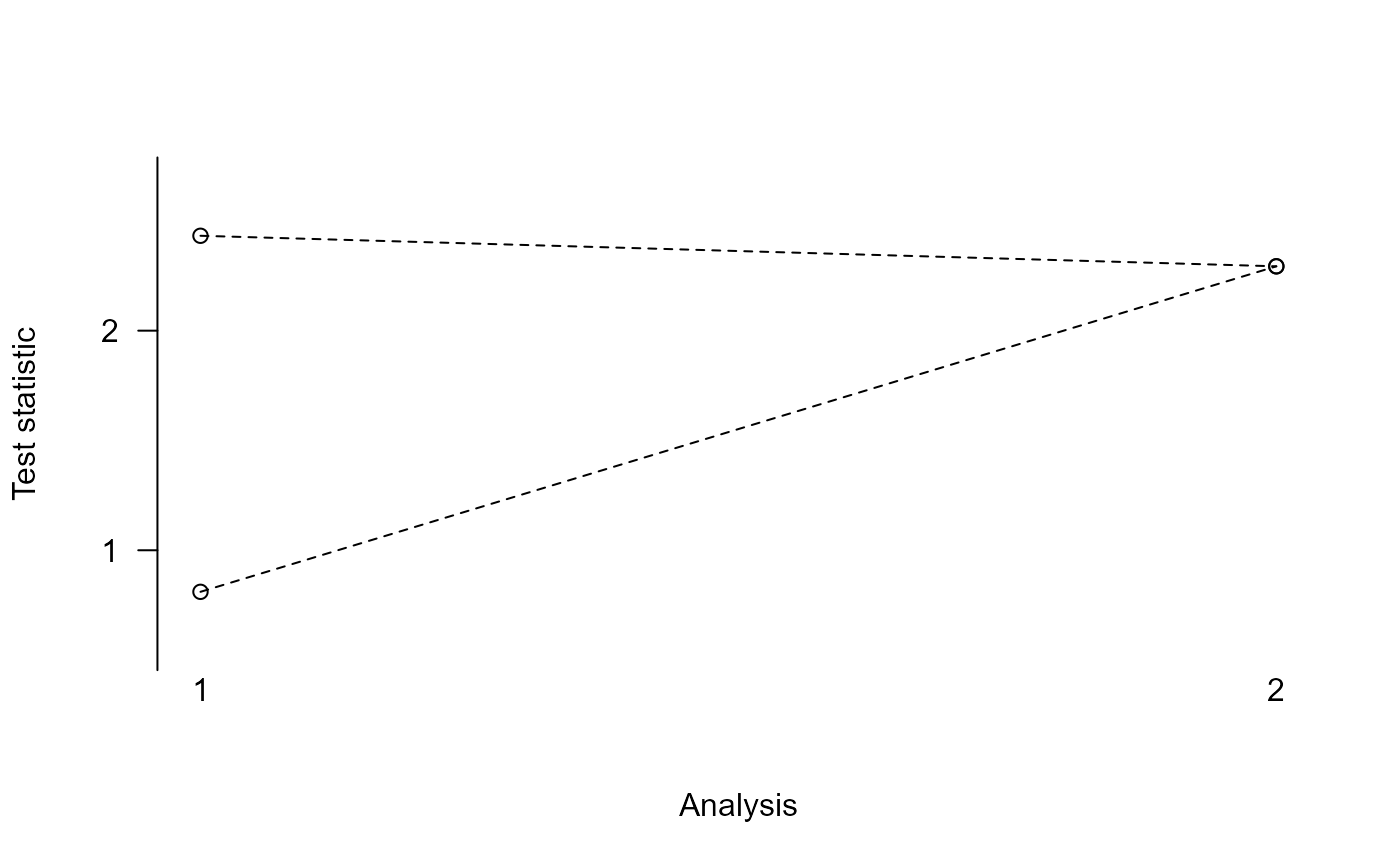
print(res)
#> Design parameters for a 2 stage trial with 4 treatments
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (control): 50 100
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (active): 50 100
#>
#> Maximum total sample size: 500
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Upper bound: 2.432 2.293
#> Lower bound: 0.811 2.293
summary(res)
#> Design parameters for a 2 stage trial with 4 treatments
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (control): 50 100
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (active): 50 100
#>
#> Maximum total sample size: 500
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Upper bound: 2.432 2.293
#> Lower bound: 0.811 2.293
plot(res)
 res <- mams.sim(nsim=10000, nMat=matrix(c(44, 88), nrow=2, ncol=5), u=c(3.068, 2.169),
l=c(0.000, 2.169), pv=c(0.65, 0.55, 0.55, 0.55), ptest=c(1:2, 4))
print(res)
#> Simulated error rates based on 10000 simulations
#>
#>
#> Prop. rejecting at least 1 hypothesis: 0.930
#> Prop. rejecting first hypothesis (Z_1>Z_2,...,Z_K) 0.908
#> Prop. rejecting hypotheses 1 or 2 or 4: 0.928
#> Expected sample size: 346.892
# 2-stage 3-treatments versus control design, all promising treatments are selected:
res <- stepdown.mams(nMat=matrix(c(10, 20), nrow=2, ncol=4),
alpha.star=c(0.01, 0.05), lb=0,
selection="all.promising")
print(res)
#> Design parameters for a 2 stage trial with 3 treatments
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Cumulative sample size (control): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 1 ): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 2 ): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 3 ): 10 20
#>
#> Maximum total sample size: 80
#>
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 2 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 2 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 2 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 2 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.69 2.10
#> Lower boundary 0.00 2.10
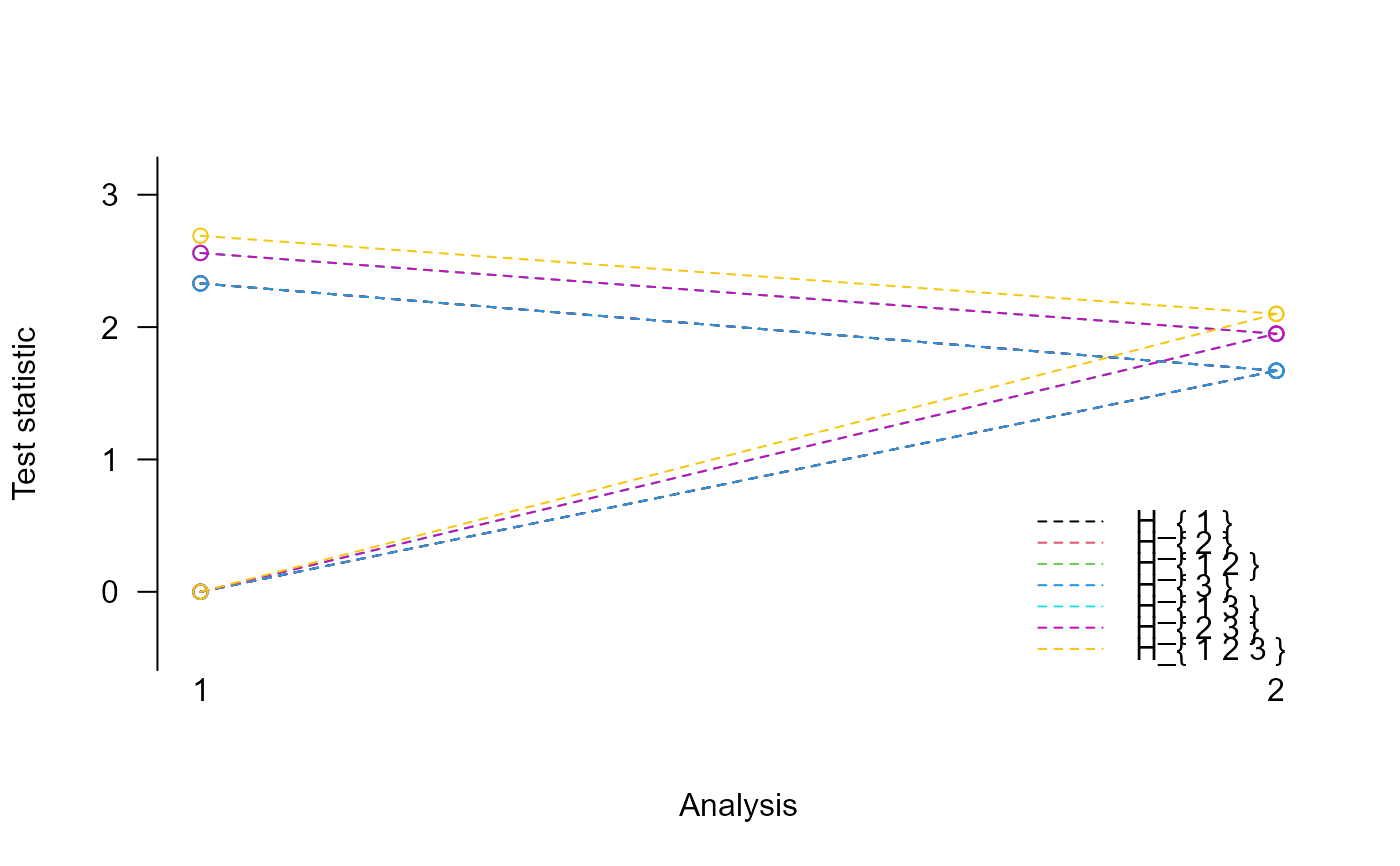
summary(res)
#> Design parameters for a 2 stage trial with 3 treatments
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Cumulative sample size (control): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 1 ): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 2 ): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 3 ): 10 20
#>
#> Maximum total sample size: 80
#>
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 2 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 2 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 2 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 2 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.69 2.10
#> Lower boundary 0.00 2.10
plot(res)
res <- mams.sim(nsim=10000, nMat=matrix(c(44, 88), nrow=2, ncol=5), u=c(3.068, 2.169),
l=c(0.000, 2.169), pv=c(0.65, 0.55, 0.55, 0.55), ptest=c(1:2, 4))
print(res)
#> Simulated error rates based on 10000 simulations
#>
#>
#> Prop. rejecting at least 1 hypothesis: 0.930
#> Prop. rejecting first hypothesis (Z_1>Z_2,...,Z_K) 0.908
#> Prop. rejecting hypotheses 1 or 2 or 4: 0.928
#> Expected sample size: 346.892
# 2-stage 3-treatments versus control design, all promising treatments are selected:
res <- stepdown.mams(nMat=matrix(c(10, 20), nrow=2, ncol=4),
alpha.star=c(0.01, 0.05), lb=0,
selection="all.promising")
print(res)
#> Design parameters for a 2 stage trial with 3 treatments
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Cumulative sample size (control): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 1 ): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 2 ): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 3 ): 10 20
#>
#> Maximum total sample size: 80
#>
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 2 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 2 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 2 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 2 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.69 2.10
#> Lower boundary 0.00 2.10
summary(res)
#> Design parameters for a 2 stage trial with 3 treatments
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Cumulative sample size (control): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 1 ): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 2 ): 10 20
#> Cumulative sample size per stage (treatment 3 ): 10 20
#>
#> Maximum total sample size: 80
#>
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 2 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 2 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.33 1.67
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.67
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 2 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.56 1.95
#> Lower boundary 0.00 1.95
#>
#> Intersection hypothesis H_{ 1 2 3 }:
#>
#> Stage 1 Stage 2
#> Conditional error 0.01 0.05
#> Upper boundary 2.69 2.10
#> Lower boundary 0.00 2.10
plot(res)
 # }
# }